Duolingo: The Smartest Business Model in Education Technology
Everybody wants to learn an exotic foreign language and be good at it for what it’s worth. And yet, the foreign language learning platforms on the web have never really picked up. That is, until the arrival of Duolingo.
What is Duolingo?
The Duolingo business model is for a person who wants to learn new languages like German, French, and others. This language learning platform has a whopping 200 million users, which they use to learn 2000 words and 8000 sentences of more than 30 different languages.
Duolingo’s services are targeted at the mass market, notably those who are interested in learning a second language but do not have the funds or time to commit to a formal language course. The platform’s courses also appeal to users who do not enjoy traditional teaching methods and instead prefer a more casual learning experience.
The users are located primarily across the Americas, Europe, and Asia. Duolingo has around 40 million active users according to a report of 2018.
History of Duolingo
Duolingo was started by Luis von Ahn in 2011. The company, headquartered in Pittsburgh, provides gamified language lessons that make learning fun and easy. You can work the lessons to fit it into your schedule. Memorize a new word when you’re stuck in traffic or two new ones as you whip up dinner, for example. But the brand’s best feature is that it is free, offering users a premium and world-class experience at zero investment.
Von Ahn grew up in Guatemala, the son of entrepreneurs who ran the country’s largest candy brand, Tropical Candy. But he never craved an entrepreneurial path. It was in 1996 when he moved to the United States to pursue his B.S. at Duke University, that he unleashed his entrepreneurial savvy. After his B.S., von Ahn earned a Ph.D. at Carnegie Mellon, and it was during this time that he became involved in several projects. His work began being consumed by millions of people, and he developed a technique that the world now knows as crowdsourcing.
Von Ahn’s best-known achievement to date has been CAPTCHA. You’ve probably encountered CAPTCHA numerous times while signing up for a website or creating an online account; it is the series of wavy letters and numbers that you are asked to type into a box to move to the next page. After working at Google for a few years, von Ahn followed a calling inspired by his childhood in Guatemala. A poor country where only the privileged have access to quality education, von Ahn decided to create a way for people to have access to education wherever they are. And the foremost step was by learning a universal language on the internet.
Duolingo business model
Like most online learning apps, Duolingo’s business model is a key ingredient to success. Let’s have a look at the complete business model of Duolingo with the market orientation.
1. Customer Segments
The targeted audience for Duolingo’s services is those who are interested notably to learn a second language or who don’t have sufficient funds to complete a regular language course.
This service provides a better learning experience who don’t like the way of the traditional method of teaching. The customers are basically from Europe, Asia, and the Americas.
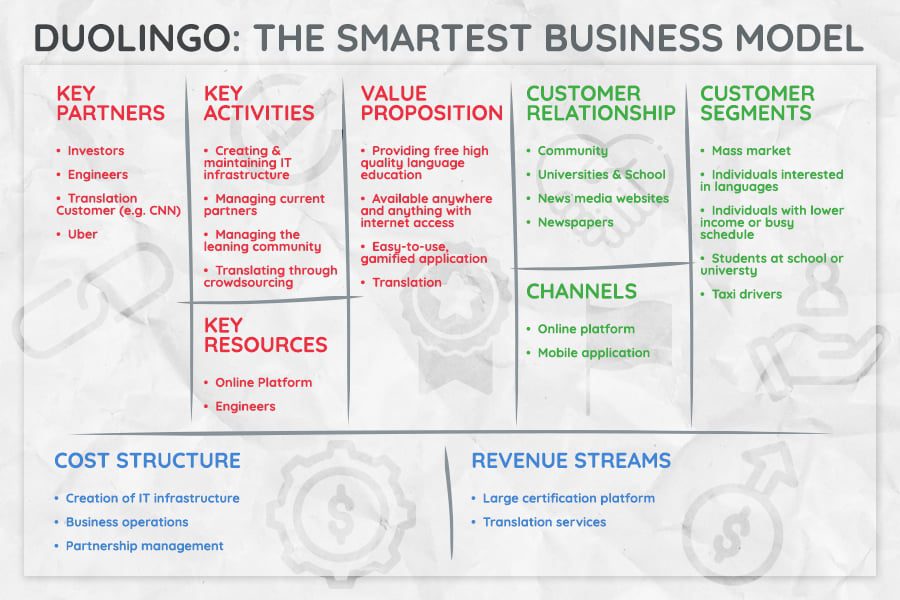
Image Source: Link
2. Value Propositions
The Duolingo provides its services with no cost high-quality language learning resources with no advertisement.
A person can access it if he/she has an active internet connection. It has cross-platform compatibility that a person can use this both in web browsers and mobile apps. It provides all the services in a non-conventional way with a gamified environment. There are also some options available for limited customization.
Other significant factors also include that it provides support for a broader user community via discussion boards.
It also provides crowdsourced translation services at a relatively low cost. The users can easily translate the sentences and can also vote on the quality of translations.
3. Key Partners
The key resources in the Duolingo business model are customer segment, relationship, mass market, an individual interested in languages, and individuals interested in lower income with busy schedules.
4. Channels
A user can access the website Duolingo or via its Apple iOS and Google play mobile apps.
5. Customer Relationships
Though Duolingo is a self-service platform, you will get all the resources once registered with the website.
It also gathers community experiences through different discussion boards and forums. The users can interact directly with each other. It allows connecting through social media accounts like Facebook, Twitter, etc. It also enables users to report issues with course material during the lessons.
6. Key activities
The computer science techniques help the courses to be more efficient and use the analytics and algorithms to deliver the content easily to the users. The language course comprises a tree of skills to complete the challenges to move on to the next section.
Duolingo manages its community of more than 100 million users.
7. Key resources
The technology data centers are the key resources particularly for the person who involved in developing and maintaining the platform. The volunteer translator for different course content has also more contributions to the company.
How to create a website like Duolingo?
Building a language learning website from scratch will be a tough task. You need a mountain of money with huge resources to develop the website. However, there are alternative cost-effective ways to create a website like Duolingo.
Find the right format of language learning websites with all the details. You can hire developers with a list of requirements for your website. Implement it technically and then take care of marketing support with the help of promotion, advertisement campaigns, etc. You can also outsource the complete development and build a complete readymade self-hosted website using a website builder.
Monetization procedure of Duolingo
Duolingo is based on a single premise: that there are 1.2 billion people in the world who are continually trying to learn a foreign language. It was this number that the brand used to establish its monetization strategy. Duolingo’s business model is one of the smartest in the technology space. The company does not charge users for course content. And because the company invests so heavily in interface and course quality, 30% of Duolingo’s users continue to use the app a week after signing up.
As a young brand, Duolingo’s real money came from translation. The company would identify pages on the internet with inadequate or non-existent translated versions; say an English Wikipedia page without a Spanish equivalent. The app would then feed sentences from these pages for multiple users to translate. For users, this would count as practice. A backend software would then sift through various translations of words in the sentence to pick a combination that fits best. Duolingo charge clients between 5 and 20 cents per word for translation, far less than the price a professional translator would have charged. In 2015, however, the brand changed course in terms of monetization.
Duolingo felt that it was moving away from its main offering by milking its translation feature. Plus, as the business grew, the team realized that they would have to invest in quality control to maintain the sanctity of translations. It was in 2015 that Duolingo adopted a new monetization strategy, by introducing a new app, called the Duolingo Test Center. The app aimed to give users a level playing field to demonstrate their language skills, without having to pay exorbitant amounts on language proficiency tests like the TOEFL or the IELTS. Duolingo priced its test at $20, one-seventh of the price you’d pay for an existing test.
How does Duolingo make money?
As we know, Duolingo gives a premium experience with an ad-free application for free of cost.
It has different revenue earning procedures that include the client base of heavy websites like CNN, Buzzfeed, etc. Duolingo helps these websites for the translation of their content with the help of crowd-sourced translation. It translates in an effective and much cheaper price.
The initial model of revenue generation was quite a cumbersome process. Thus, Duolingo has added intrusive advertisements on its website to generate revenue. This has also moved towards the freemium model and paid versions of the application with ad-free to provide a better experience.
Duolingo monetization also includes the Duolingo English Test. This certificate course provides the proficiency of English only at $49. Duolingo is always considered as a pioneer model which is, of course, a win-win scenario for the website.
Technological considerations of Duolingo
The Duolingo technology stack is hosted by an Nginx Web Server and the platform is supported by an Amazon CloudFront Content Delivery Network. Its Monitoring layer contains Rollbar and its Communications layer is composed of Google Apps and Slack. The stack also includes Mixpanel as part of its Analytics engine while Web Pack powers its Build Tools layer. Amazon SES is employed for email. It’s a given that the company has invested heavily in technology. But the language space doesn’t need a huge capital.
With technologies such as Pinlearn, a turnkey framework that allows lightning-fast setup, small and medium-sized businesses are claiming their share of the market by spending about 100 times less on the launch.
Pinlearn’s tech stack is composed of:
- Laravel 5.3 (PHP)
- Angular JS 1
- MySQL
- Redis cache
- NGINX web server
- SSL
- JQuery
- Bootstrap
Marketing of Duolingo
Duolingo has spent little to none on marketing since its inception. It has always leveraged its engagement with users for word-of-mouth traffic. When you have 150 million users aged between 7 and 95, that’s quite something. Von Ahn is modeling the marketing approach of Duolingo on that adopted by Microsoft many decades ago; minimal marketing and maximum results. Von Ahn does, however, believe in furthering reach by growing a following. For instance, in April 2011, he delivered a TED talk about CAPTCHA that was watched by 2 million people. This is a great strategy for new-age businesses to emulate. With the money saved on technologies like Pinlearn, you can set aside a reasonable budget for digital marketing campaigns.
Language is increasingly being used as a ticket to a better life across the globe. It’s no wonder that a plethora of brands have entered the online education software space. Rosetta stone gives direct competition to Duolingo, but it is a paid service. The website offers three downloadable packages, with varying benefits, priced at €192.50, €238 and €279.30. Similarly, Babbel, a German language learning platform follows a subscription model for its language courses. It gives customers the option to choose amongst a monthly, three-monthly, six-monthly and an annual plan. The higher the plan value, the better the value for money. Babbel also offers a 20-day money-back guarantee, in a bid to win the confidence of users.
In a slightly different approach, British online course learning platform Busuu is the largest, first-of-its-kind social network for language. The platform connects learners with native speakers, engaging them in real conversations. Busuu comes in two formats; the free version offers flashcards, writing exercises and corrections from native speakers and the premium version comes equipped with quizzes, grammar exercises, offline mobile apps, and a vocabulary trainer, in addition to myriad other features. Busuu provides plans for 1 month, 6 months, 12 months and 24 months, priced at $9.99 per month, $9.49 per month, $5.83 per month and $5.41 per month respectively.
Takeaway
The online language landscape is so vast that it will take years to fully capitalize on the opportunities available. Customizing the app to fit the learner’s language and scaling the language offerings available provide infinite permutations for entrepreneurs to venture. With the world shrinking, thanks to the internet, language barriers need to be broken, and online language learning could be the solution.





